√ダウンロード hazard ratio vs odds ratio vs relative risk What is the difference between odds ratio and hazard ratioThis is called the odds ratio;The risk difference of A relative to B is 001, the risk ratio is 101 Or one could view the risk ratio and the odds ratio as approximations to the hazard ratio or rate ratio Rates and hazards can exceed 1, unlike risks , so there's no constraint on the hazard ratio , unlike the risk ratio

Crude And Adjusted Measures Of Odds Ratio Or And Hazard Ratio Hr Download Table
Hazard ratio vs risk ratio vs odds ratio
Hazard ratio vs risk ratio vs odds ratio-5 comments share save hide report 86% Upvoted This thread is archived New comments cannot be posted and votes cannot be cast Sort by bestBryan E Dowd, PhD;




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk
Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literature Most readers perceive it as relative risk (RR), although most of them do not know why thatOdds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinction becomes important in cases of mediumThe risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a ) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions
Celle utilisée pour les paris sportifs Dans notre exemple la cote chez les personnes exposées est de 30 contre 70 Chez les non exposés, cette cote est de 10 pour 90 Ainsi l'OR est égal àOdds Ratio Odds Ratio for comparing two proportions OR >Odds Ratio Das Odds Ratio OR ist eine Maßzahl die z B zur Beschreibung eines Therapie Wirkungsunterschiedes genutzt wird Der Odds (engl Chance) ist ein Wahrscheinlichkeitquotient aus der Wahrscheinlichkeit, dass das Ereignis eintrifft, zu der Wahrscheinlichkeit, dass das Ereignis nicht eintrifft Der Odds mit einem WürfelWurf z B eine 6 zu werfen, beträgt
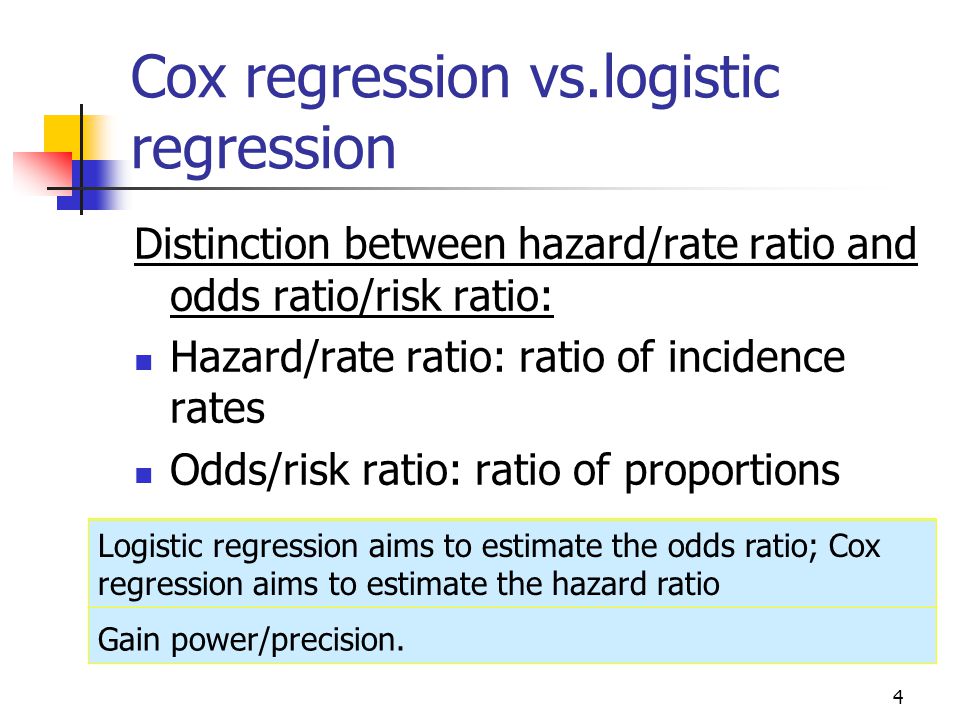
James H McAuley, PhD To the Editor Dr Norton and colleagues 1 described significant limitations of odds ratios (ORs) but they did not report one importantRatio and odds ratio/risk ratio – Hazard/rate ratio ratio of incidence rates – Odds/risk ratio ratio of proportions By taking into account time, you are taking into account more information than just binary yes/no Gain power/precision Logistic regression aims to estimate the odds ratio;Hazard Ratios vs Risk Ratios (or Relative Risk) Hazard ratio is frequently interpreted as risk ratio (or relative risk), but they are not technically the same However, if that helps you to understand hazard ratio then it is OK But keep in mind HR is not RR One of the main differences between risk ratio and hazard ratio is that risk ratio does not care about the timing



Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar
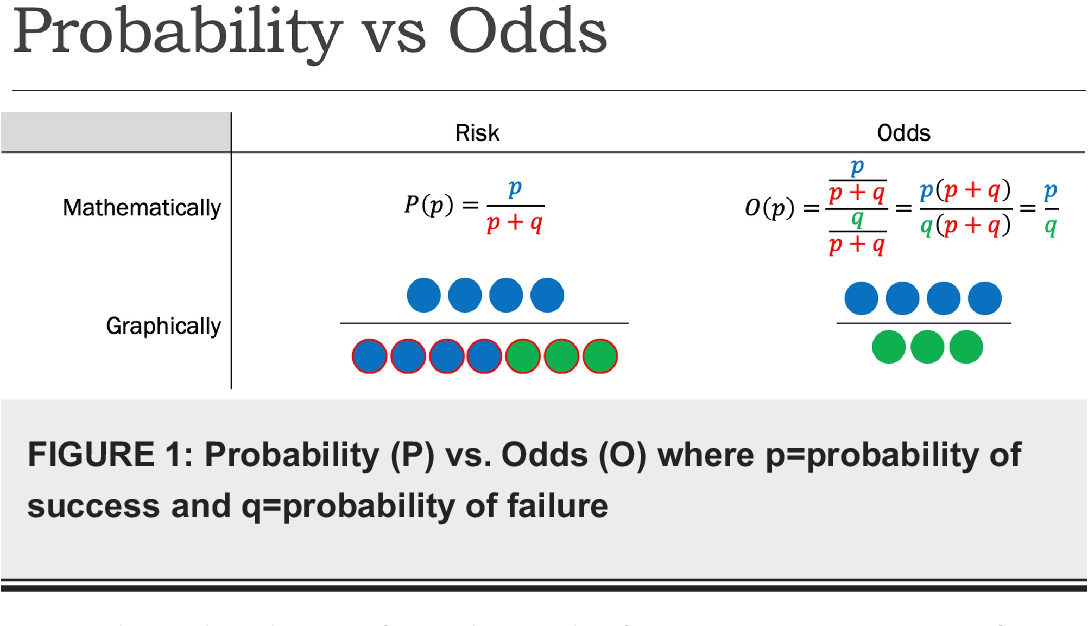
Thanks and Regards Fred Jeremy Miles unread, ,RISK AND ODDS DEFINITIONS "Risk" refers to the probability of occurrence of an event or outcome Statistically, risk = chance of the outcome of interest/all possible outcomes The term "odds" is often used instead of risk "Odds" refers to the probability of occurrence of an event/probability of the event not occurring At first glance, though these two concepts seemIf odds ratios are reported in an RCT or cohort study, be cautious to not interpret it as a risk ratio;




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




Crude And Adjusted Measures Of Odds Ratio Or And Hazard Ratio Hr Download Table
L'Odds Ratio (OR) est le rapport des cotes d'exposition Cette notion de cote est semblable àHazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereof Hazard ratios suffer somewhat less from selection bias with respect to the endpoints chosen and can indicate risks that happen beforeDos conceptos estadísticos muy usuales en el lenguaje de la Medicina son el concepto de Odds ratio (Ver el tema dedicado a las Medidas de la relación entre variables cualitativas) y el concepto de Hazard ratio (Ver los temas dedicados al Análisis de supervivencia y a la Regresión de Cox ) Vamos a delimitar uno y otro a través de un ejemplo que




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download
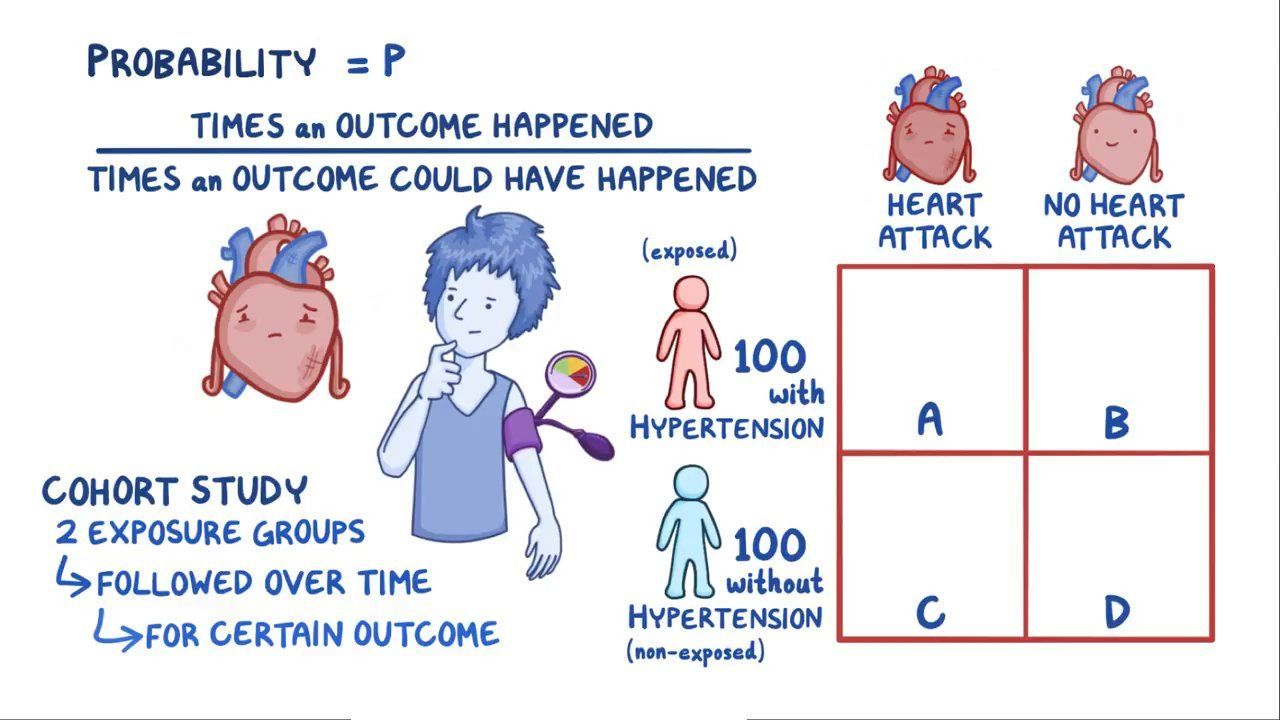
Understanding Relative Risk, Odds Ratio, and Related Terms As Simple as It Can Get Chittaranjan Andrade, MD ABSTRACT Risk, and related measures of effect size (for categorical outcomes) such as relative risks and odds ratios, are frequently presented in research articles Not all readers know how these statistics are derived and interpreted, nor are all readers aware of their strengths andOdds Ratios vs Risk Ratios—Reply Edward C Norton, PhD;Odds ratio vs risk ratio You know the difference between risk and odds A risk is the proportion of subjects with an event in a total group of susceptible subjects Thus, we can calculate the risk of having a heart attack among smokers (infarcted smokers divided by the total number of smokers) and among nonsmokers (the same, but with non




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow



Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Biostatistics Wiki Ucsf
Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a rHazard ratio VS Odds ratio Close 5 Posted by 2 years ago Archived Hazard ratio VS Odds ratio Does HR measure the probability of death, whereas OR measures the risk of developing a disease??That's not actually a proper formula for the risk ratio or odds ratio In fact, given only the minor allele frequencies in cases and controls and no counts, we can't actually compute the OR or RR Yet in this case I actually gave a very close approximation of the odds ratio because for very rare alleles, a «




How Did Researchers Calculate The Hazard Ratio Cross Validated




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology
More on the Odds Ratio Ranges from 0 to infinity Tends to be skewed (ie not symmetric) "protective" odds ratios range from 0 to 1 "increased risk" odds ratios range from 1 to Example "Women are at 144 times the risk/chance of men" "Men areFor any level of risk or odds under no exposure, multiplication by a risk or odds ratio less than 1 will produce a risk or odds given exposure that is possible 0 to 1 for risks and 0 to infinity for odds Thus, a constant risk or odds ratio is possible for ratios less than 1 If the risk ratio comparing exposed persons with those not exposed is greater than 1, the ratio can beRisk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results 1 A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios 2, while a 12 paper found



Odds Ratio Osmosis




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
The odds ratio is a common measure of risk but its interpretation may be hazardous The risk ratio is a ratio of probabilities, which are themselves ratios The numerator of a probability is the number of cases with the outcome, and the denominator is the total number of cases Leave a Reply Cancel reply Your email address will notAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy &1 increased risk of group 1 compared to 2 OR




Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk
Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three common, but often misused, statistical measures in clinical research In this paper, the authors dissect what each of these terms define, and provide examples from the medical literature to illustrate each of these statistical measures Finally, the correct and incorrect methods to use these measures are summarizedOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome Methods Casecontrol studies are quite common in medical studies Hazard ratio (HR) is nearly the same measure often quoted Relative risk or RR is very common in the literature, but may representIf there was an extremely low proportion ofAn odds ratio of 2 means that the event is 2 time more probable given a oneunit increase in the predictor It means the odds would double, which is not the same as the probability doubling In Cox regression, a hazard ratio of 2 means the event will occur twice as often at each time point given a oneunit increase in the predictor




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Odds Ratio Article
Is odds ratio a measure of risk?Odds Ratio vs Relatives Risiko Das relative Risiko (RR) ist einfach die Wahrscheinlichkeit oder Beziehung zweier Ereignisse Nehmen wir an, A ist Ereignis 1 und B ist Ereignis 2 Man kann das RR erhalten, indem man B von A oder A / B dividiert Genau so kommen Experten auf populäre Zeilen wie Gewöhnliche alkoholische Getränketrinker sind 24 mal mehr gefährdet, an LeberproblemenOdds Ratio, Hazard Ratio and Relative Risk Janez Stare1 Delphine MaucortBoulch2 Abstract Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literature Most readers perceive it as relative risk (RR), although most of them do not know why that would be true But since such perception is mostly



A Population Based Cohort Study Of Socio Demographic Risk Factors For Covid 19 Deaths In Sweden Nature Communications




Thread By Profdfrancis Risk Ratio Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio 2nd And Final Part Of The Tweetorial From Orbita Hq Fun Easy And Informativ Meded Foamed Cardiology Cardiotwitter
When the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075 If the risks were 08 and 09,Risk (hazard) ratios and odds ratios cannot be used interchangeably in metaanalysis Like euro and pound they have to be converted into the same value eg Swedish crowns You find theRisk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results 1 A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




Measures Of Association Ppt Download
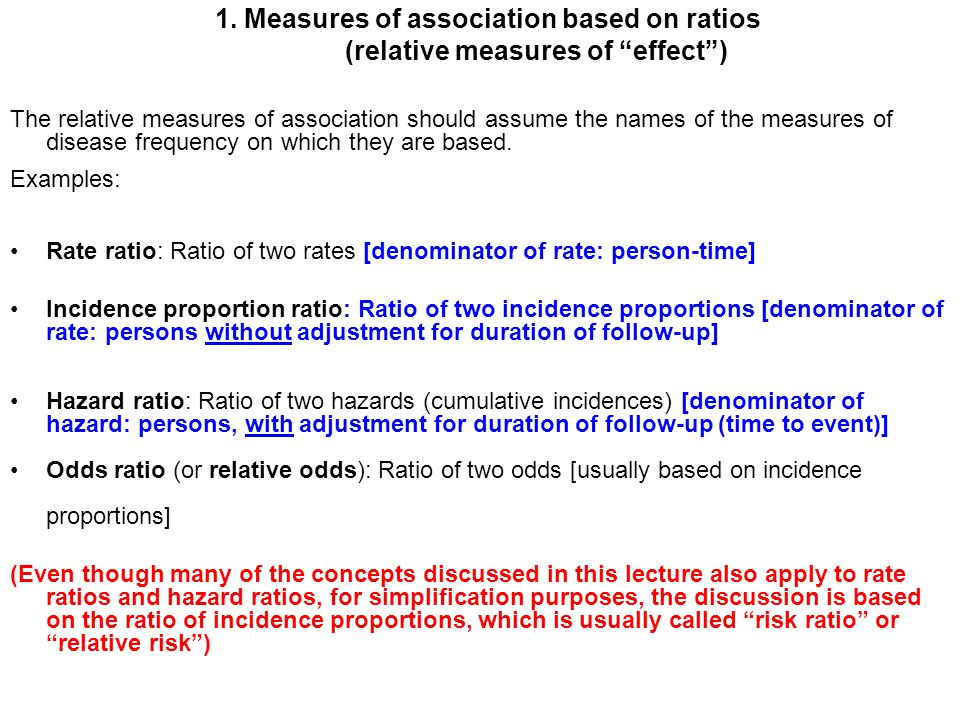
C and b «d, so (a/(ac))/(b/(bd)) ≈ (a/c)/(b/d) = (ad)/(bc) Suppose that theCox regression aims to estimate the hazard ratio 10 Risks vs Rates Relationship between risk andHazard ratios are measures of association widely used in prospective studies (see later) It is the result of comparing the hazard function among exposed to the hazard function among nonexposed As for the other measures of association, a hazard ratio of 1 means lack of association, a hazard ratio greater than 1 suggests an increased risk, and




Introduction To Cox Regression Kristin Sainani Ph D




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood
Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find that increasing the incidence will increaseOdds ratios While risk reports the number of events of interest in relation to the total number of trials, odds report the number of events of interest in relation to the number of events not of interest Stated differently, it reports the number of events to noneventsThe basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



Who Saw This In The San Francisco Chronicle In The Past Week Ppt Download
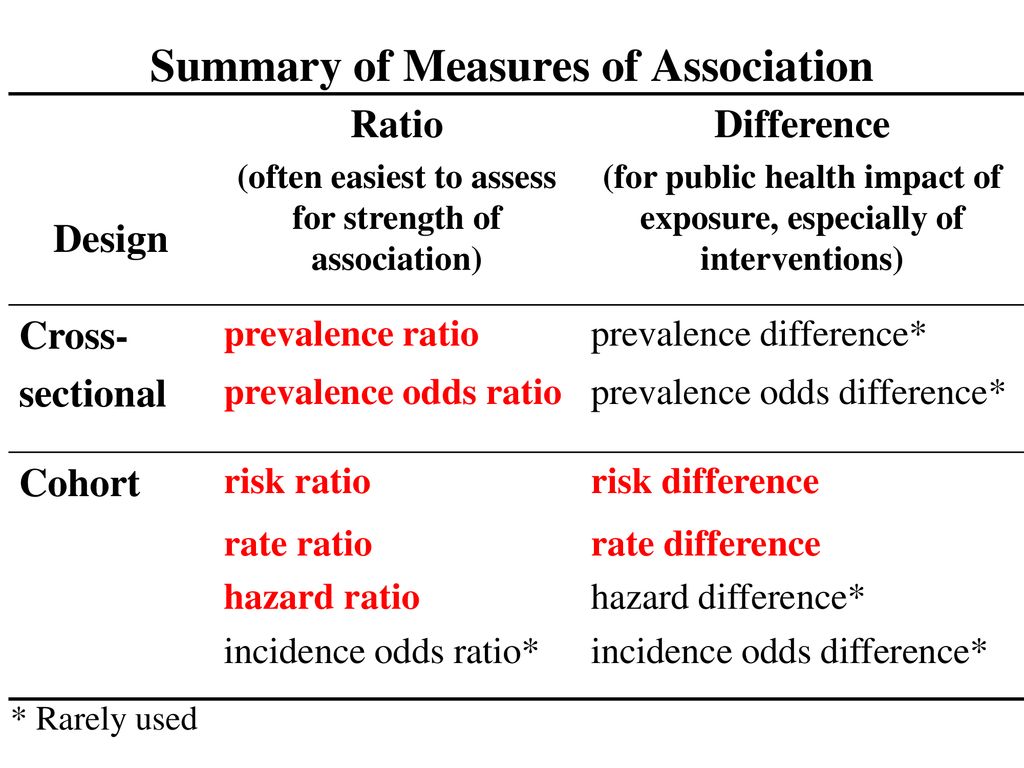
Especially if the outcome is not rare or the odds ratio is far from 1 5,6 Conclusion In this paper, we have explained how to calculate and interpret the risk and rate difference, number needed to treat, risk and rate ratio, odds ratio and hazard ratio in different study designsRelative Risk vs Odds ratioRobert D Herbert, PhD;



Relative Risk Wikipedia




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube
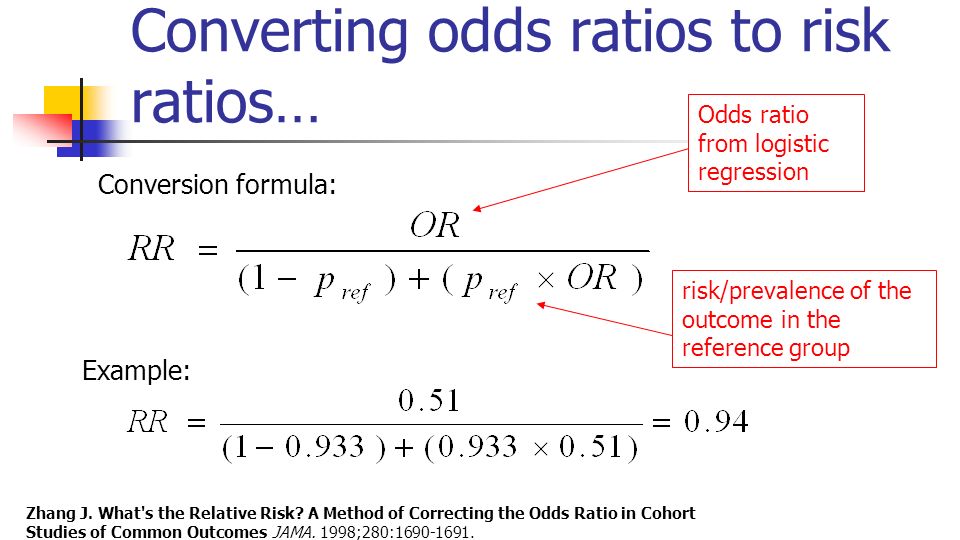
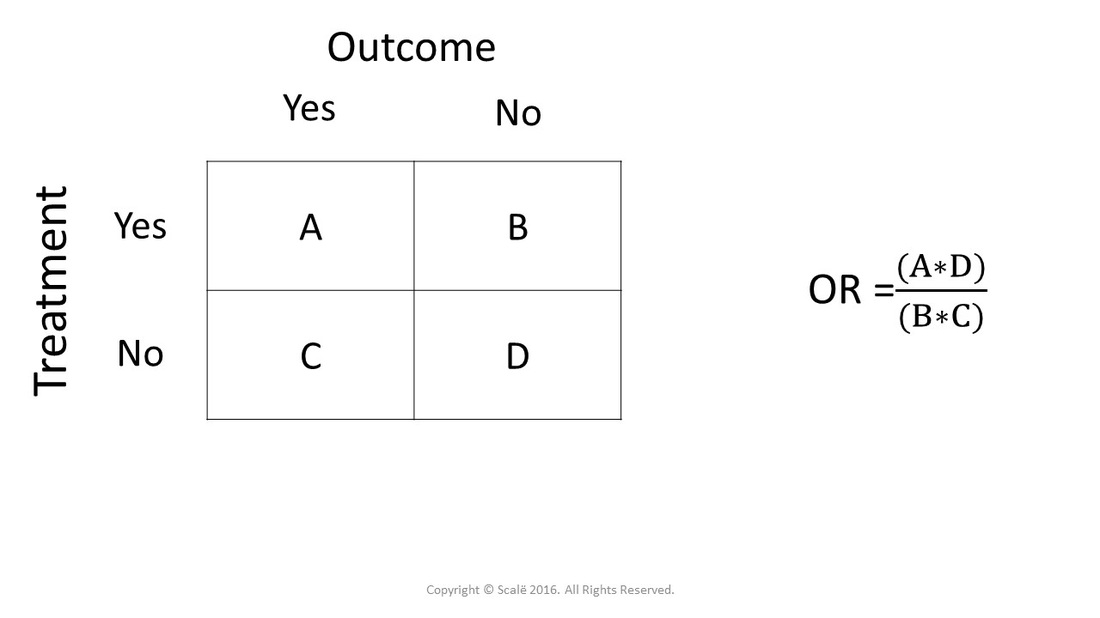
Matthew L Maciejewski, PhD JAMA Guide to Statistics and Methods Mediation Analysis Hopin Lee, PhD;Odds ratio = (A*D) / (B*C) The relative risk tells us the ratio of the probability of an event occurring in a treatment group to the probability of an event occurring in a control group It is calculated as Relative risk = A/ (AB) / C/ (CD) In short, here's the difference An odds ratio is a ratio of two oddsOdds ratios approximate risk ratios when the outcome under consideration is rare but can diverge substantially from risk ratios when the outcome is common In this paper, we derive optimal analytic conversions of odds ratios and hazard ratios to risk ratios that are minimax for the bias ratio when outcome probabilities are specified to fall in any fixed interval



1



Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像
Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinctionThe hazardSafety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsOdds ratio vs Relative Risk/Hazard Ratio I have a background in physics with a few courses in statistics, but I still have a hard time intuitively understanding OR I get RR as it just is a ratio of probabilities, and I look at HR as RR with a time component Every time I see an OR, though, I have to look up the incidence and just calculate what the RR would be (which I don't even know to be




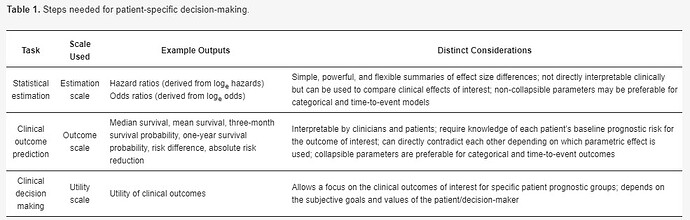
Assessing Heterogeneity Of Treatment Effect Estimating Patient Specific Efficacy And Studying Variation In Odds Ratios Risk Ratios And Risk Differences Statistical Thinking




Crude And Adjusted Measures Of Odds Ratio Or And Hazard Ratio Hr Download Table
Odds that a person with an adverse outcome was at risk (or exposed)/ Odds that a person without an adverse outcome was at risk (or exposed) Odds group 1/odds group 2As odds ratio and hazard ratio are the approximation to the relative risks, but they could be adjusted in multivariable settings When conducting a meta analysis, for the same disease and exposure, if publications report those three, also their adjusted values, then what we need in the final meta analysis?Ratio and odds ratio/risk ratio – Hazard/rate ratio ratio of incidence rates – Odds/risk ratio ratio of proportions By taking into account time, you are taking into account more information than just binary yes/no Gain power/precision Logistic regression aims to estimate the odds ratio;




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora
Odds Ratio Vs Risiko Relatif Ketika dua kelompok sedang dipelajari atau diamati, Anda dapat menggunakan dua ukuran untuk menggambarkan kemungkinan komparatif dari suatu peristiwa terjadi Dua ukuran ini adalah rasio odds dan risiko relatif Keduanya adalah dua konsep statistik yang berbeda, walaupun begitu banyak saling terkait satu sama lainOdds vs risk ratio Odds ratio vs hazard ratio vs risk ratio INTRODUCTION Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) isOdds Ratios vs Risk Ratios Posted on by StatsBySlough From the previous post, we understand that Odds Ratios (OR) and Risk Ratios (RR) can sometimes, but not always be interpreted in the same way We even saw that scientific studies made the mistake of interpreting odds ratios as risk ratios




Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
A terminology problem odds ratio versus odds Author William Gould, StataCorp James Hardin, StataCorp Unfortunately, the language used to describe statistical terms is not used uniformly across fields One example of this is odds and odds ratio Economists especially refer to what others call the odds as the odds ratio Below, we will be careful to define our terms Proof that
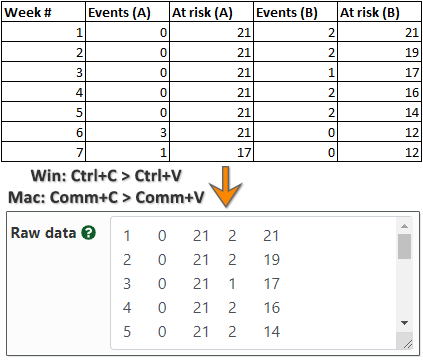



Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value



Hazard Ratio




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Biostatistics Primer What A Clinician Ought To Know Hazard Ratios Sciencedirect




Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Pdf What Are Hazard Ratios




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Clinical Trials In Hours Point Estimation Odds



2




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training




Ppt Measures Of Association Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Who Saw This In The San Francisco Chronicle In The Past Week Ppt Download



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora



1



2




Estimated Relative Risk Odds Ratio Or Hazard Ratio With 95 Ci For 4 Download Scientific Diagram



Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference The Journal Of Family Practice Data Science Study Plan Clinical Trials




Calculating The Risk Ratio Odds Ratio And Risk Difference In A Randomised Controlled Trial Youtube
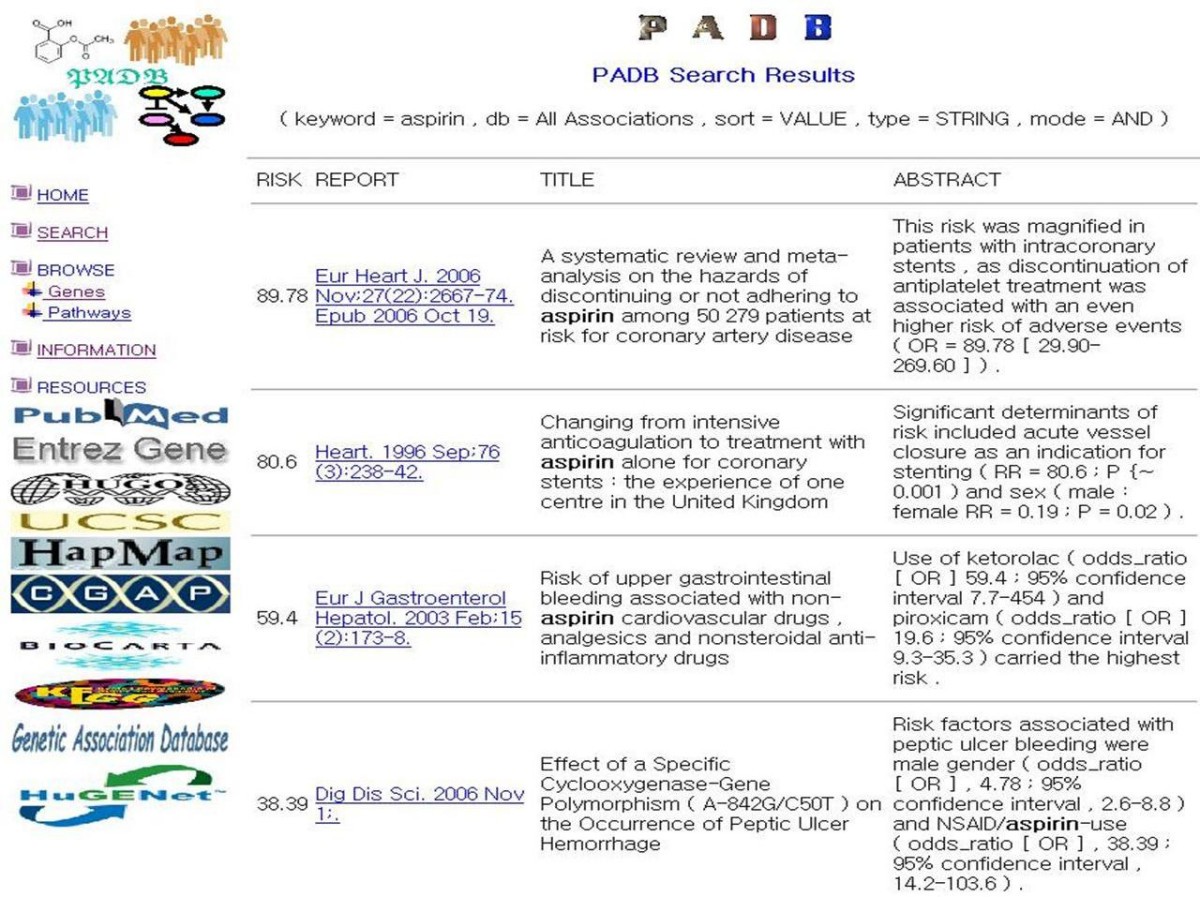



Padb Published Association Database Bmc Bioinformatics Full Text




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Eposters How Big Is A Big Hazard Ratio




In A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Estimates From Observational Studies Can I Pool Or With Hr And Rr Probably Not How Can I Transform Hr To Or




Ppt Point Estimation Odds Ratios Hazard Ratios Risk Differences Precision Powerpoint Presentation Id




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Use And Interpret Chi Square In Spss




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table



Measures Of Association Ppt Download




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




Relative Risk Wikipedia
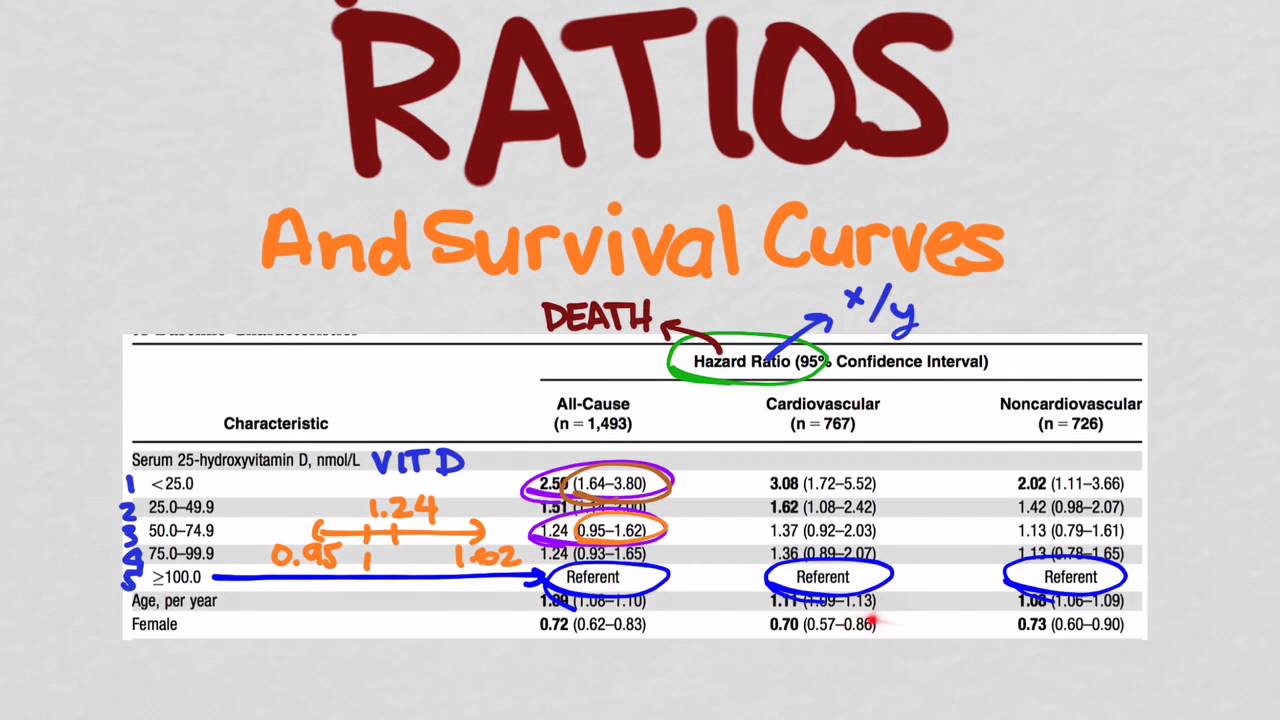



Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube



Should One Derive Risk Difference From The Odds Ratio Bayes Datamethods Discussion Forum




Approximate Reciprocal Relationship Between Two Cause Specific Hazard Ratios In Covid 19 Data With Mutually Exclusive Events Medrxiv
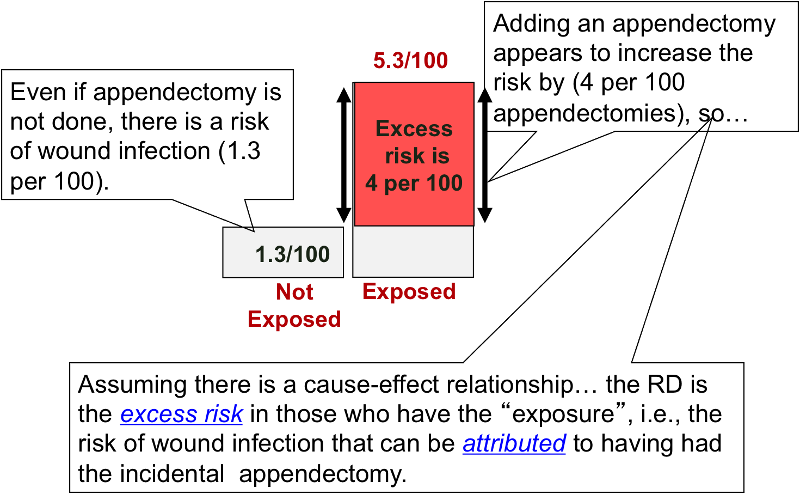



Risk Differences And Rate Differences




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Confidence Intervals And P Values




Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect




Measures Of Disease Association Ppt Download




Graphical Presentation Of Relative Measures Of Association The Lancet



1




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar
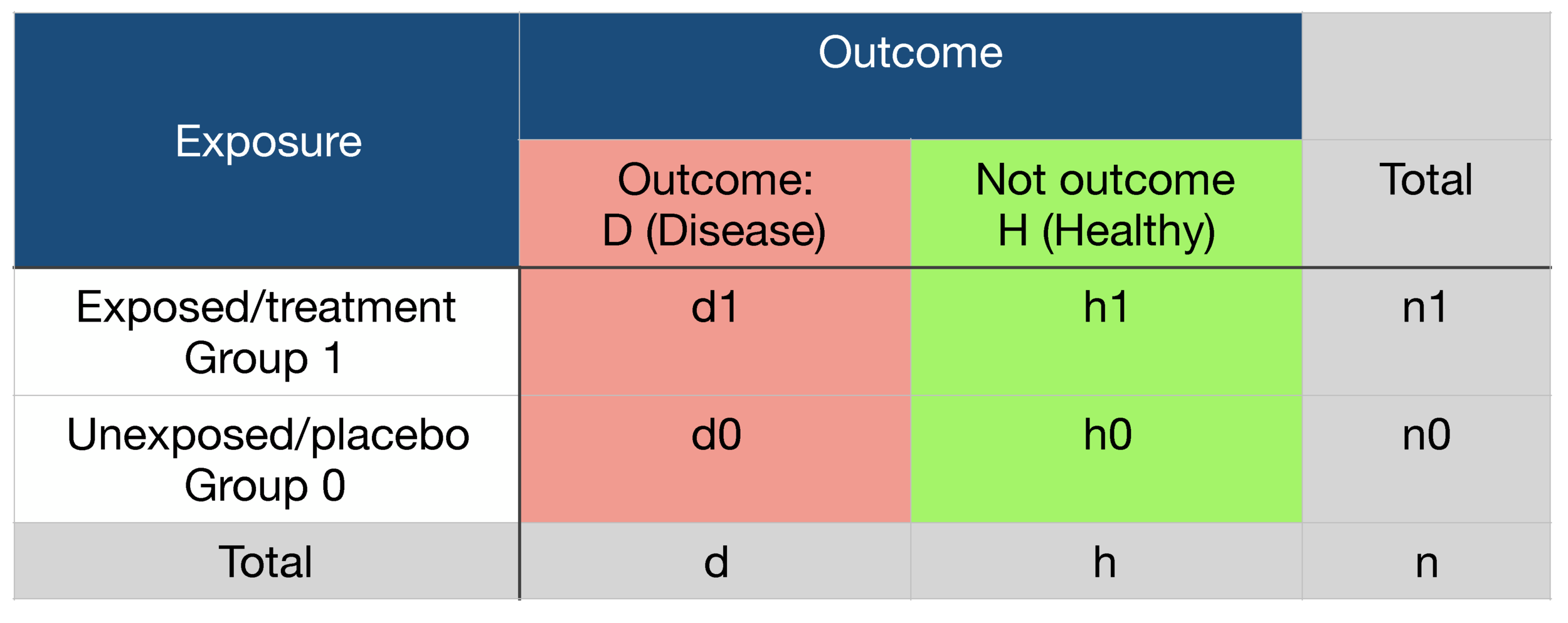



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gpraj



How To Remember The Differences Between Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Likelihood Ratio And In What Instances They Should Be Applied Quora




Applied Interpretation Of Clinical Studies Jim Hoehns Pharm D ps Fccp Ppt Download




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Statistics 103 Monday July 10 17 Survival Analysis




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk




Hazard Ratio Wikipedia




Ppt Relative Risk Increased Risk And Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id




Statistics For Afp Dr Mohammad A Fallaha Afp
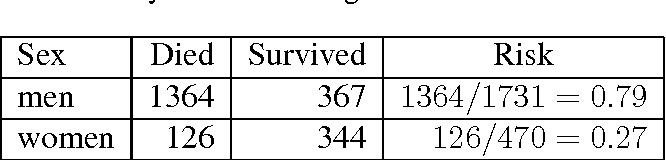



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International
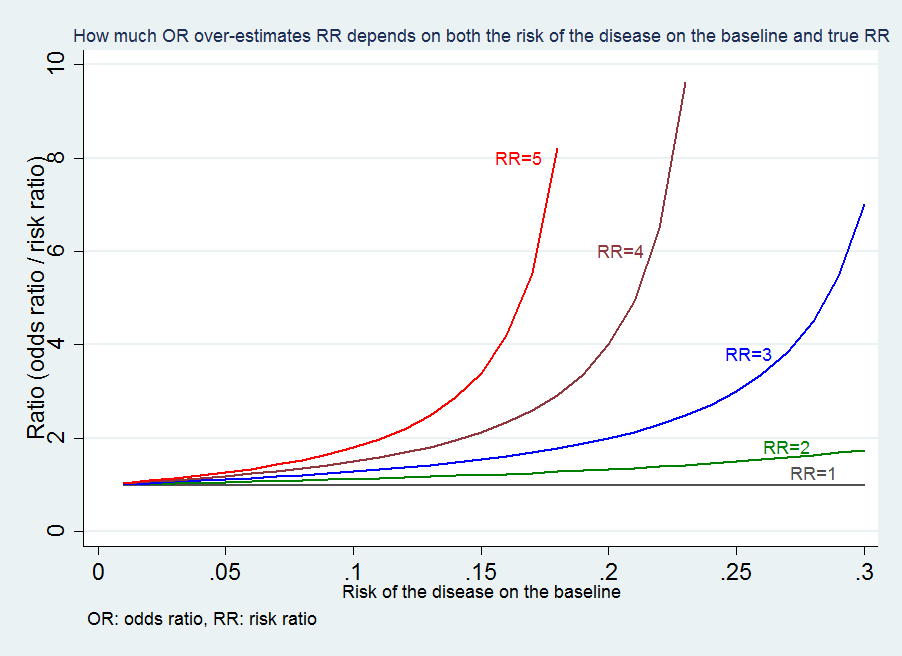



Medical Statistics And Data Science Statistics



No comments:
Post a Comment